What Is Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer. Head and neck cancers can have many different names depending on where the cancer starts. Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control.
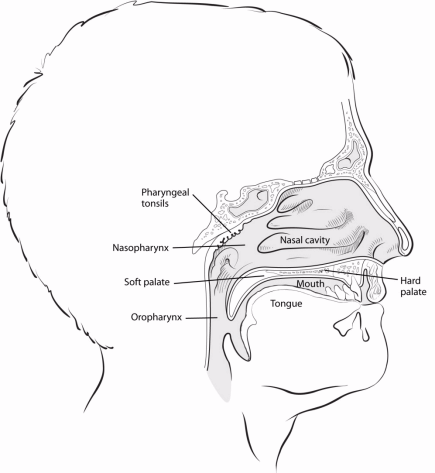
Nasopharyngeal cancer starts in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose and near the base of skull.
Since the head and neck area has so many organs in a small place, knowing what type of head and neck cancer you have can be confusing. Ask your doctor to write down the exact kind of cancer you have and show you where it is on a picture. To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer?
The nasopharynx
The nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat (pharynx) that lies behind the nose and nasal cavity. It's a box-like chamber about 3/4 inches (2 cm) wide and 1½ inches (4 cm) long. It lies just behind the nasal cavity and above the soft part of the roof of the mouth (soft palate). It is located in the upper part of the pharynx. The oropharynx is just below the nasopharynx and the hypopharynx is just below the oropharynx.
The nasopharynx serves as a passageway for air traveling from the nose to the throat.
To see more details of the nasopharynx, explore the 3D interactive color model below.
Types of nasopharyngeal tumors
Several types of tumors can develop in the nasopharynx. Some of these tumors are benign (not cancer), and others are malignant (cancer). It's important to talk with your doctor about what type of tumor you might have.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)
The most common cancer in the nasopharynx is nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Carcinoma is cancer that starts in the cells that line the surfaces of organs in the body, called epithelial cells.
There are different types of NPC. They all start from epithelial cells that line the nasopharynx, but the cells of each type look different when looked at closely in the lab:
- Keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type in places with low rates of NPC, like the US.
- Non-keratinizing differentiated carcinoma is less common in areas with high rates of NPC and is often associated with the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV).
- Non-keratinizing undifferentiated carcinoma is the most common type in areas with high rates of NPC and is often associated with EBV.
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma is rare and very aggressive.
The treatment is the same for all types of NPC, but the stage of the cancer (how far it has grown and spread) is often more important than the type in predicting a person's outlook (prognosis). Research is being done to evaluate using EBV DNA levels to also help predict a person’s outlook (prognosis), when the NPC is linked to EBV.
Other cancers in the nasopharynx
Other types of cancers can also be found in the nasopharynx:
- About 5% of cancers that start in the nasopharynx are lymphomas. They are cancers of immune system cells called lymphocytes, which are found throughout the body, including in the nasopharynx. See Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma to learn more.
- Sarcomas and melanomas make up less than 5% of cancers that start in the nasopharynx. These cancers don't start in epithelial cells like the other types of NPCs. See Soft Tissue Sarcoma and Melanoma Skin Cancer for more about these cancers.
Benign nasopharyngeal tumors
Benign nasopharyngeal tumors are fairly rare and tend to develop in children and young adults. These tumors do not spread to other parts of the body and are usually not life-threatening. They include tumors or malformations of the vascular (blood-carrying) system, such as angiofibromas and hemangiomas, and benign tumors of minor salivary glands within the nasopharynx.
Benign nasopharyngeal tumors don't always need treatment. When they do, the treatment is not the same as for nasopharyngeal cancer. If you have a benign tumor, ask your doctor what to expect.
- Written by
- References

The American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as editors and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
Chang ET, Ye W, Zeng YX, Adami HO. The Evolving Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021;30(6):1035-1047. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1702.
Leeman JE, Katabi N, Wong RJ, Lee NY and Romesser PB. Ch. 65 - Cancer of the Head and Neck. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff’s Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Pa. Elsevier; 2020.
Mohanty S, Gopinath M, Subramanian M. Benign tumours of nasopharynx-revisited. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;65(Suppl 1):22-25. doi:10.1007/s12070-011-0384-6.
Thompson L. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006;85(2):74.
Last Revised: August 1, 2022
American Cancer Society medical information is copyrighted material. For reprint requests, please see our Content Usage Policy.
American Cancer Society Emails
Sign up to stay up-to-date with news, valuable information, and ways to get involved with the American Cancer Society.


