Embolization Therapy for Liver Cancer
Embolization therapy injects substances directly into an artery in the liver to block or reduce the blood flow to a tumor in the liver.
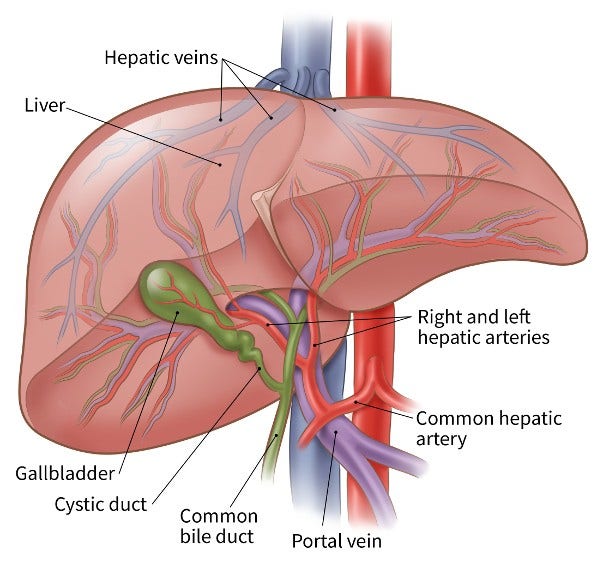
The liver has 2 blood supplies. Most normal liver cells are fed by the portal vein, whereas cancer in the liver is mainly fed by the hepatic artery. Blocking the part of the hepatic artery that feeds the tumor helps kill off the cancer cells, but it leaves most of the healthy liver cells unharmed because they get their blood supply from the portal vein.
When is embolization used to treat liver cancer?
Embolization is an option for some people with liver tumors that cannot be removed by surgery. It can be used for people with tumors that are too large to be treated with ablation (usually larger than 5 centimeters, or about 2 inches, across) and who also have adequate liver function. It can also be used along with ablation. This treatment is sometimes used in people waiting for a liver transplant.
While embolization can sometimes be helpful, in general it is not used by itself to try to cure liver cancer.
Embolization can reduce some of the blood supply to the normal liver tissue, so it may not be a good option for some people whose liver has been damaged by diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
It isn’t yet clear which type of embolization has a better long-term outcome.
People getting this treatment typically do not need to stay in the hospital overnight.
Trans-arterial embolization (TAE)
During TAE, a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) is put into an artery in the inner thigh through a small cut and eased up into the hepatic artery in the liver. A dye is usually injected into the bloodstream to help the doctor watch the path of the catheter.
Once the catheter is in place, small particles are injected into the artery to plug it up, blocking oxygen and key nutrients from the tumor.
Trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE)
TACE is usually the first type of embolization used for large liver cancers that can’t be treated with surgery or ablation. It combines embolization with chemotherapy (chemo).
Most often, this is done by giving a chemo drug through the catheter directly into the artery, then plugging up the artery, so the chemo can stay close to the tumor.
Drug-eluting bead chemoembolization (DEB-TACE)
DEB-TACE combines TACE with drug-eluting beads (tiny beads that contain a chemo drug). The procedure is essentially the same as TACE except that the artery is blocked after drug-eluting beads are injected. Because the chemo is physically close to the cancer and because the drug-eluting beads slowly release the chemo, the cancer cells are more likely to be damaged and die.
The most common chemo drugs used for TACE or DEB-TACE are cisplatin and doxorubicin.
Radioembolization (RE)
Radioembolization combines embolization with radiation therapy. This is done by injecting small beads (called microspheres) that have a radioactive isotope (yttrium-90 or Y-90) attached to them into the hepatic artery.
Once infused, the beads lodge in the blood vessels near the tumor, where they give off small amounts of radiation to the tumor site for several days. The radiation travels a very short distance, so its effects are limited mainly to the tumor.
Possible side effects of embolization
Possible complications after embolization include:
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Infection in the liver
- Blood clots in the main blood vessels of the liver
Sometimes, it can take several weeks to fully recover from the procedure. Because healthy liver tissue can be affected, there is a risk that liver function will get worse after embolization. This risk is higher if a large branch of the hepatic artery is embolized.
Serious complications are not common, but they are possible.
- Written by
- References

Developed by the American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team with medical review and contribution by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Abdalla EK, Stuart KE, Singal AG. Overview of treatment approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. UpToDate. 2024. Accessed at https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-treatment-approaches-for-hepatocellular-carcinoma on December 9, 2024.
Curley SA, Stuart KE, Schwartz JM, Carithers RL, Hunter KU. Localized hepatocellular carcinoma: Liver-directed therapies for nonsurgical candidates not eligible for local thermal ablation. 2024. Accessed at https://www.uptodate.com/contents/localized-hepatocellular-carcinoma-liver-directed-therapies-for-nonsurgical-candidates-not-eligible-for-local-thermal-ablation on December 9, 2024.
Fong Y, Covey AM, Feng M, Daneng L. Ch 36. Cancer of the Liver. In: DeVita VT, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA, eds. DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; 2023: 36:544-569.
National Cancer Institute. Primary Liver Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version. Accessed at https://www.cancer.gov/types/liver/hp/adult-liver-treatment-pdq on September 11, 2024.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®): Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Version 3.2024. Accessed at https://www.nccn.org/ on December 9, 2024.
Pérez-López A, Martín-Sabroso C, Gómez-Lázaro L, Torres-Suárez AI, Aparicio-Blanco J. Embolization therapy with microspheres for the treatment of liver cancer: State-of-the-art of clinical translation. Acta Biomaterialia. 2022.
Last Revised: February 11, 2025
American Cancer Society medical information is copyrighted material. For reprint requests, please see our Content Usage Policy.
American Cancer Society Emails
Sign up to stay up-to-date with news, valuable information, and ways to get involved with the American Cancer Society.


